There may be a decrease in retail inflation in February
There may be a decrease in retail inflation in February: there is some relief due to the decrease in the prices of food items, but the inflation rate will continue today
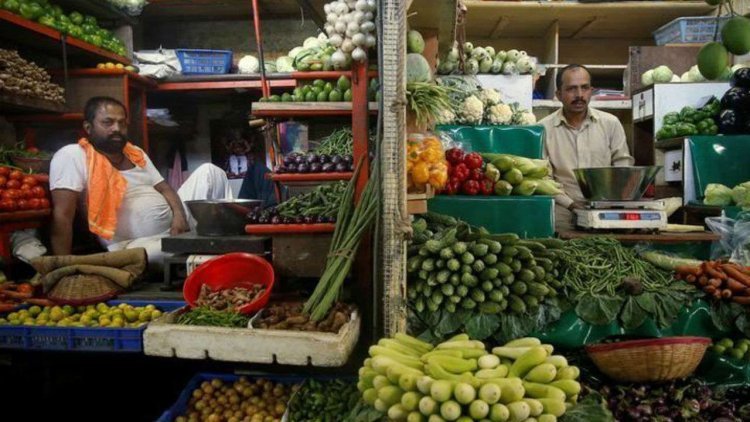

Today i.e. on March 13, the inflation rate (CPI) figures for February will be released. The inflation rate is expected to decrease in February due to a slight reduction in the prices of food items. Food items account for about half of the consumer price index (CPI) basket. In the last month, the prices of food grains like wheat have decreased in the international and domestic markets. The government has also increased the supply. Its effect will be seen in the retail inflation figures.
Retail inflation in the country had risen to 6.52% in the month of January. This was the highest level of retail inflation in three months. It stood at 5.72% in December 2022 and 5.88% in November 2022. Three months ago in October 2022, retail inflation was 6.77%. Whereas in January last year, it was 6.01%.
Kunal Kundu, the economist at Societe Generale, said inflation is unlikely to rise much for the next few quarters. But the pace of its reduction will be slow. The effect of the more than 10% fall in the rupee last year can also be seen in inflation.
Barring food items and energy, there is currently no visible decline in core inflation. According to economists, it will remain above the limit of 6% in February. Due to this, there is no possibility of laxity in the monetary policy of RBI. Interest rates may increase further.
Inflation is directly related to purchasing power. For example, if the inflation rate is 7%, then Rs 100 earned will be worth only Rs 93. That's why investing should be done keeping this in mind inflation. Otherwise, the value of your money will decrease.
The rise and occurrence of inflation depend on the demand and supply of the product. If people have more money, they will buy more things. Buying more things will increase the demand for things and if there is no supply according to the demand, the price of these things will increase.
In this way, the market becomes vulnerable to inflation. Simply put, an excessive flow of money in the market or a shortage of goods causes inflation. On the other hand, if the demand is less and the supply is more, then the inflation will be less.
To reduce inflation, the flow of money (liquidity) in the market is reduced. For this, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) increases the repo rate. Worried about rising inflation, RBI has recently increased the repo rate by 0.25%. Due to this the repo rate has increased from 6.25% to 6.50%.
Many economies worldwide consider WPI (Wholesale Price Index) as their basis for measuring inflation. This does not happen in India. In our country, along with WPI, CPI is also considered a scale to check inflation.
The Reserve Bank of India considers retail inflation, not wholesale prices, as the main standard for setting monetary and credit-related policies. WPI and CPI affect each other in the nature of the economy. In this way, if WPI increases, then CPI will also increase.
Apart from crude oil, commodity prices, and manufactured cost, many other factors play an important role in determining the retail inflation rate. There are about 299 items on the basis of whose prices the rate of retail inflation is fixed.
For Latest News update Subscribe to Sangri Today's Broadcast channels on Google News | Telegram | WhatsApp





































.jpeg)













































































.jpeg)














